Europe's gas market: Understanding market mechanisms and developing strategies
What role does gas play in the energy transition and how can it help to balance out the fluctuations of renewable energies? What mechanisms drive price developments in the energy markets – especially in the gas market? How can companies understand market volatility and use it to their strategic advantage? And what measures can purchasers take to secure their energy supply and optimize costs in the face of uncertainties? We answer these and other questions to provide you with orientation and practical approaches for dealing with the challenges of the energy markets.
The role of gas in the changing energy markets and the energy transition
Energy markets have undergone massive upheaval in recent years. Above all, the urgency of reducing CO₂ emissions is bringing gas into the focus of the energy transition. As a relatively flexible energy source, it can not only help solve the intermittency problem of renewable energies, but also constitute an appealing alternative to coal for electricity production.
At the same time, geopolitical tensions are significantly influencing market mechanisms. The Covid-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine have caused major upheaval in the European gas market, forcing countries to quickly reduce their dependence on Russian supplies.
Europe's gas infrastructure: separating transport and supply
Following the liberalisation of the energy markets in the early 2000s, strict separation was stablished between the management of gas infrastructures (transport, storage, distribution, etc.) and the upply of gas itself. Although the Dutch market is now the most active and serves as a benchmark, each European country has its own place in the market. This is where sellers (producers and importers) and buyers - gas suppliers such as ENGIE or large industrial consumers - come together.
The role of these wholesale markets is to:
- give a price signal that reflects the balance between supply and demand;
- provide reliable and transparent information to guide future investments;
- make gas exchanges between countries more fluid and secure, by offering suppliers the possibility of managing their imbalances on a day-to-day basis.
In Europe, natural gas and electricity were historically traded OTC (Over The Counter) through bilateral agreements, generally with adaptable conditions (volume profile, delivery points, etc.), but not without credit risk. Large trading platforms (e.g. ICE) have rapidly emerged with standard products (flat profile, hub delivery), transparent price reporting and solutions to cover counterparty risk through collateral and margin calls.
Different gas markets
As with electricity, there are different types of gas markets:
Forward Market
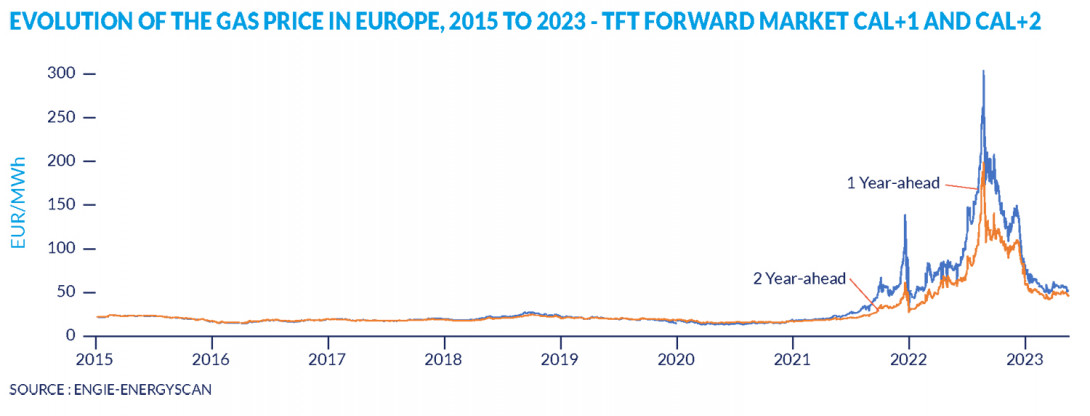
As the name suggests, the forward market allows you to buy gas for deferred delivery. The price is then negotiated on the date of the contract and determined on the forward market. This is a win-win situation for both the consumer and the distributor: the purchase price is clearly defined and the supplier knows the precise quantity of gas to be supplied. The European gas price index, which is used as a reference on the stock markets, is called the “TTF ICE Endex”. It shows the price that different players are willing to pay to buy or sell gas on a specific delivery date.
Gas market: Development of gas prices in Europe, 2015 to 2023 – TTF futures market CAL+1 and CAL+2
Spot Market
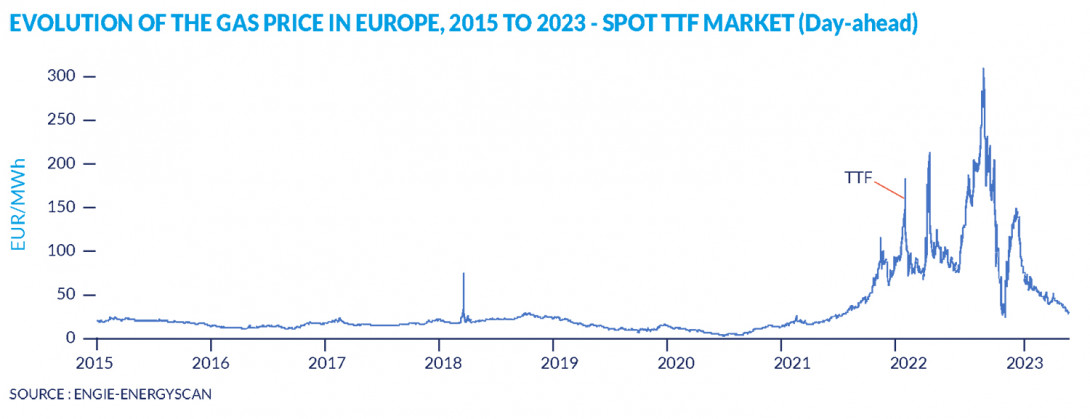
It is also possible to buy gas on the spot market - the short-term market - also known as the “day-ahead market”. It is then delivered on the same day or the next day. Prices are set in the same way as on the forward market, the only difference being the very short time between purchase and delivery of the gas.
Gas market: Development of gas prices in Europe, 2015 to 2023 – Spot TTF market (day-ahead)
Gas Supply, Transport and Storage
Production in Europe
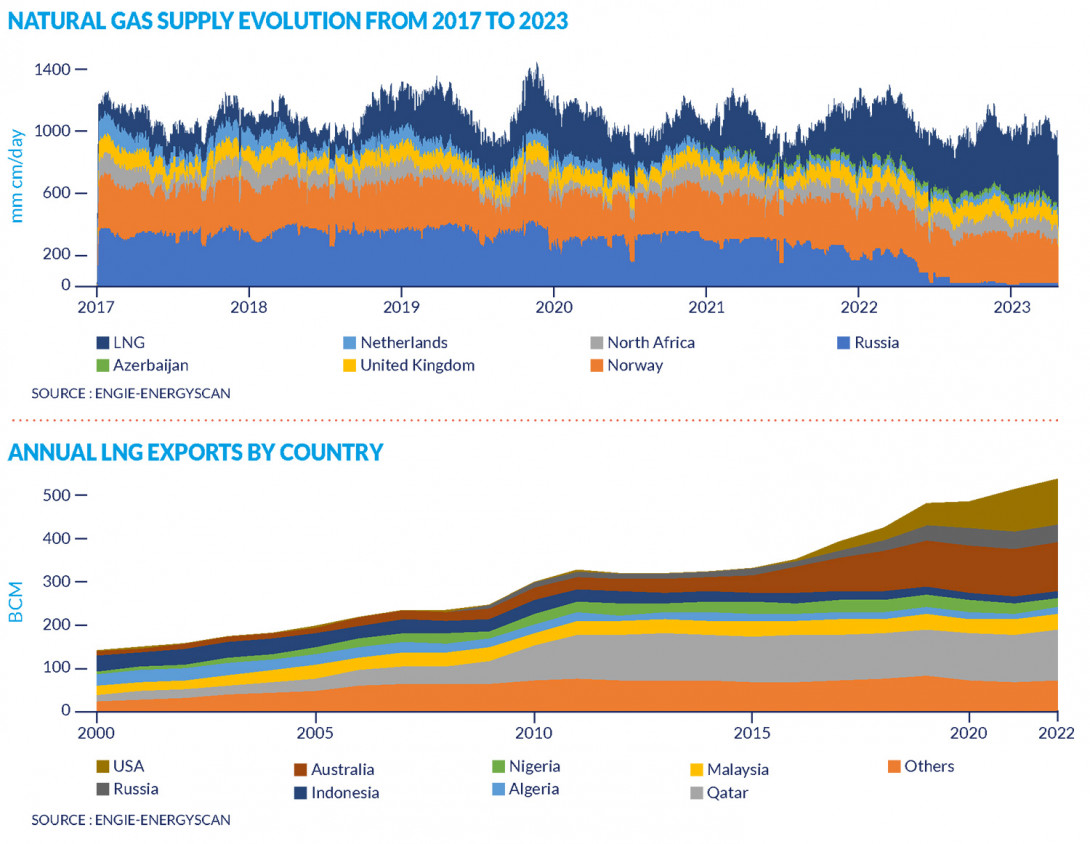
Only one third of the natural gas consumed in Europe is produced on the continent:
- in the United Kingdom or in the Netherlands, although this production has decreased;
- in Norway, which remains a reliable and stable producer.
Gas market: Development of natural gas supply from 2017 to 2023
Importe
Production outside Europe Two thirds of the gas we consume in Europe comes from imports. This is far from negligible when you consider that the gas market, unlike the electricity market, is global. International factors, such as geopolitical tensions, rising gas demand in China or falling production in the United States, for example, can therefore have a direct influence on market prices in Europe.
Gas market: Annual LNG exports by country from 2000 to 2022
Transport
- Transport by pipeline Gas, in gaseous form, is extracted from production sites in Norway and North Africa and then sent directly into the system. It flows through pipelines at 90 bar to supply the countries of Europe.
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is the condensation of natural gas into a liquid state, which allows it to be transported by sea. In 2022 LNG, mainly from the United States, Qatar and Russia, represented 36 % of the total European gas supply. Thanks to the development of LNG transported by ship, Europe has access to more gas production and can now diversify its sources of supply.
Gas market: Annual LNG exports by country from 2000 to 2022
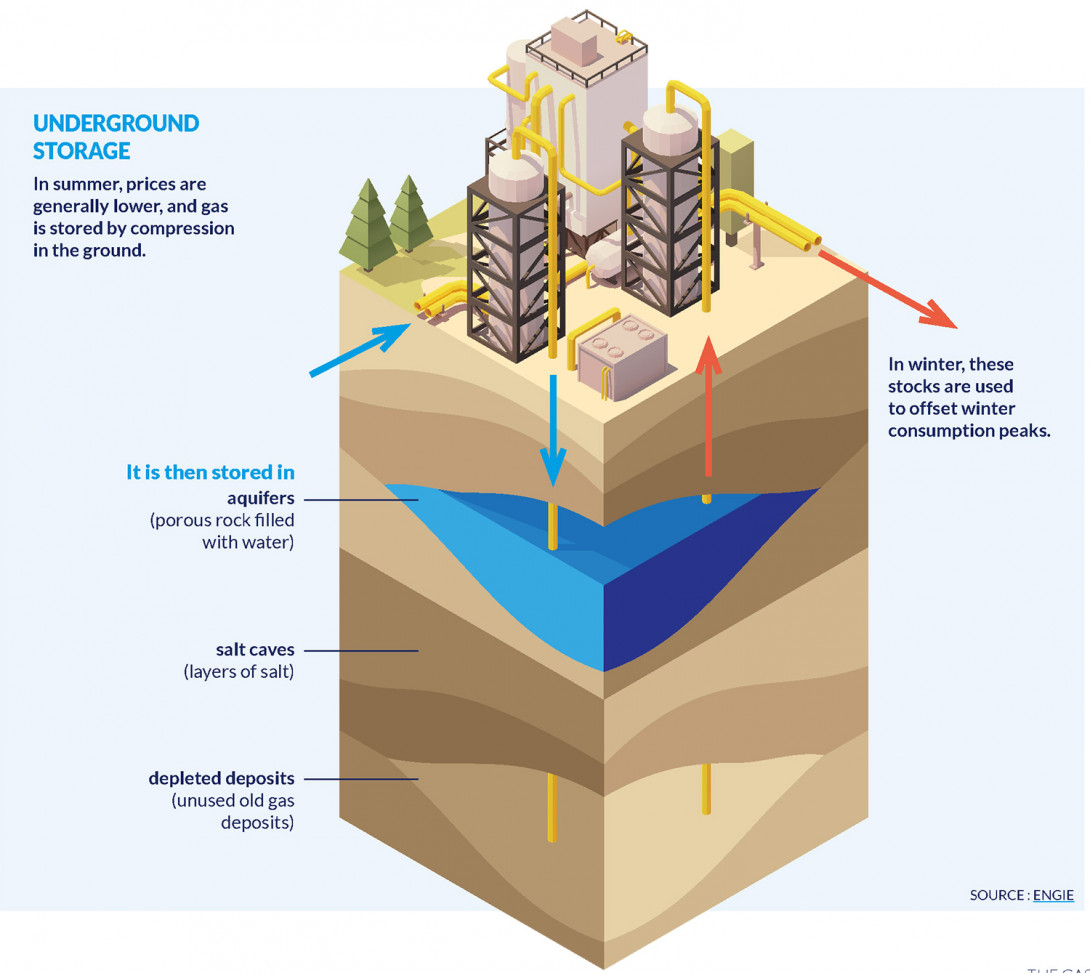
Storage
Unlike electricity, natural gas can be stored in large volumes. This makes it an ideal source of energy for dealing with peak consumption in winter. The tanks are filled in the summer, when demand - and therefore prices - are normally at their lowest. The stored gas is then fed back into the grid for the heating period.
Underground gas storage
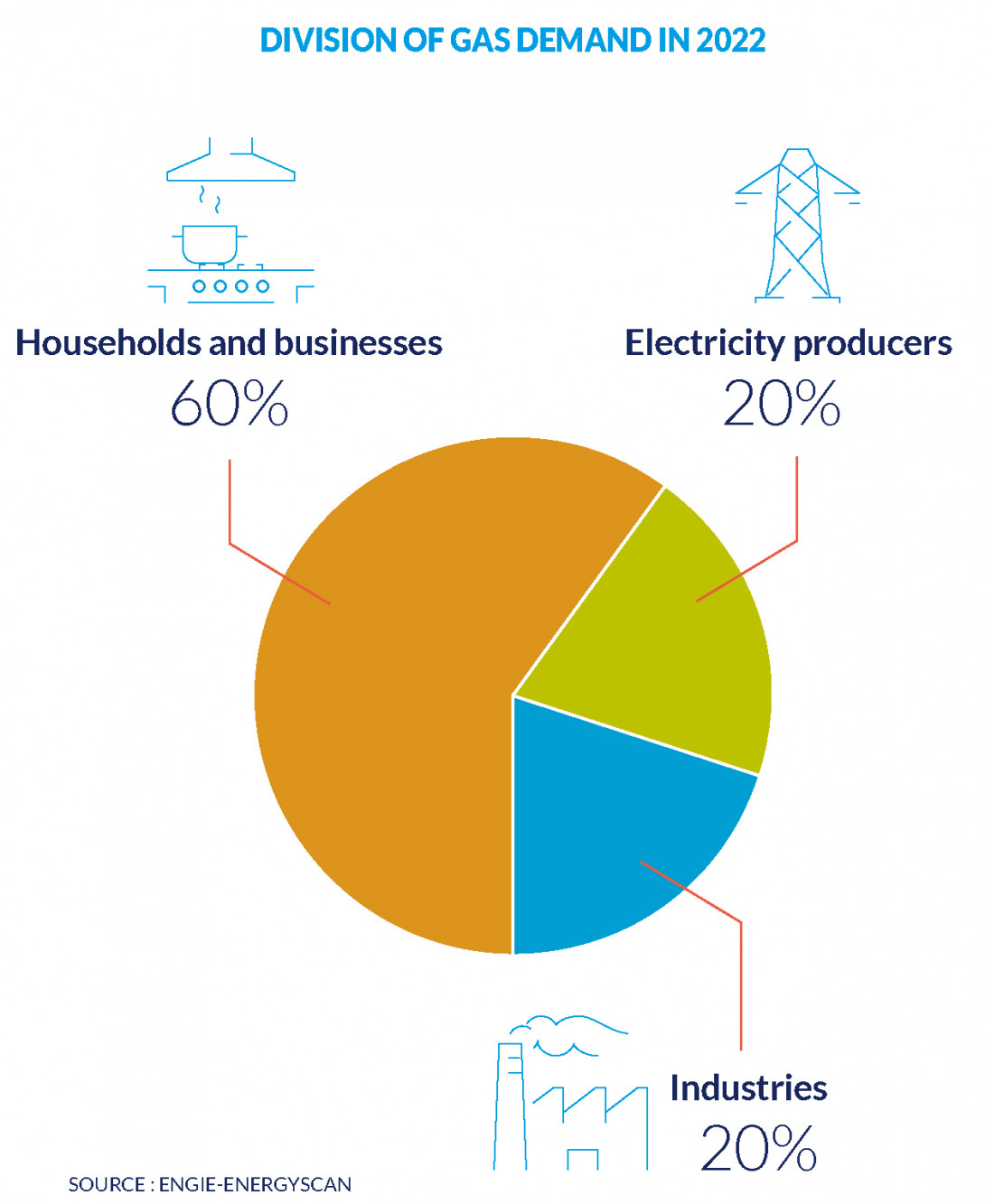
Gas consumers: Households and businesses, electricity producers and manufacturers
Household and businesses
For heating and domestic consumption.
Electricity Producers
For power plant supply.Natural gas, in combination with other energy sources, is used to power the power plant’s turbine, which in turn drives an alternator to produce electricity. With the development of new generation power plants, the proportion of electricity produced using this method has greatly increased.
There are two reasons for this:
- natural gas emits half as much CO2 as coal;
- it guarantees stability of the electricity network in the event of consumption peaks or renewable energy insufficiencies.
As a major player in the energy transition, ENGIE has chosen to gradually replace its conventional power plants, which are largely coal-fired, with combined-cycle gas plants and cogeneration units.
Manufacturers
Depending on the sector of activity, natural gas is used for different purposes:
- for heating or combustion, in the food industry for example;
- as a raw material in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
As manufacturers only have a few alternative production technologies, they are particularly vulnerable to the volatility of market prices.
Distribution of gas demand in 2022
What determines the market price?
Factors influencing the demand for gas
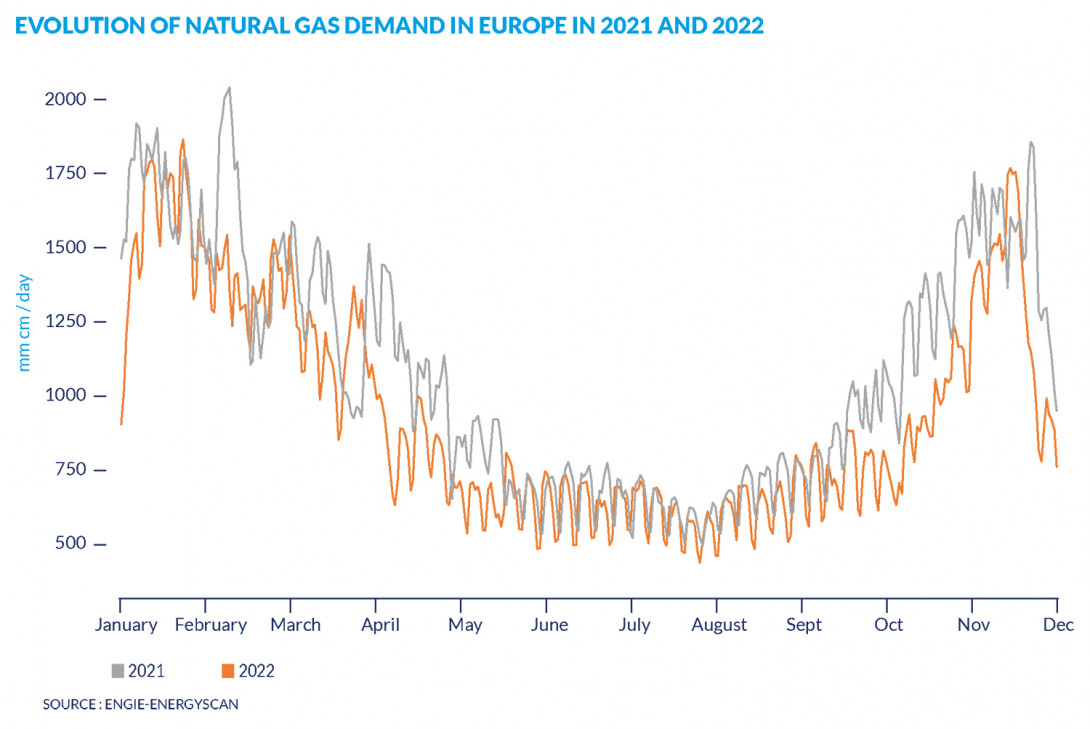
- Renewable generation
As solar or wind generation decreases, the demand for gas to produce electricity increases. Since gas is often used to generate electricity, demand is closely linked to developments in the electricity market. A change in electricity demand has a direct effect on the demand for the raw materials needed to generate it, and thus also on gas demand – but in a specific order. This is known as the 'merit order'.
- The price of raw materials used to produce electricity
The lower the price of coal relative to gas, the more it will be used in preference.
- Climate and the weather
The lower the temperature, the higher the need for heating.
- Demand for electricity
As the two markets are closely linked, an increase in demand for electricity automatically leads to an increase in demand for gas.
- The price of gas
The higher the price of gas, the lower the demand.
Gas market: Development of natural gas demand in Europe in 2021 and 2022
The gasprice
The price of gas, expressed in megawatt-hours (MWh), is the result of gas supply and demand on the wholesale market. It therefore depends on a number of factors, such as the level of production, the availability of infrastructure, economic dynamism, weather variations, etc. But the gas price does not depend solely on the wholesale market price. Other costs, such as the cost of transport and use of gas infrastructures, and taxes, are also added to it.
Follow the market trends
Once you have a clear energy strategy, follow market and gas prices closely. Like financial investments, a strategy is only useful if you take advantage of all the opportunities that arise later.
How do you monitor market trends?
- Keep an eye on macro-economic trends and geopolitical developments: this will allow you to anticipate and understand changes in the financial markets, as well as in the energy markets (mainly for oil).
- Follow the financial markets. They are an indicator of economic activity, and therefore of energy demand.
- Watch oil prices. Their price variation influences gas prices. When the price of oil rises, demand for gas, which will have become relatively cheaper, rises - as does its price.
- Save time with expert analysis. At ENGIE, we make sure we share our expertise with you to help you detect opportunities for your business. We have set up a number of free tools for this purpose.
Efficient energy management: Understand the gas market and act strategically
A clear purchasing strategy and regular market monitoring are crucial. Understand the gas market: what factors influence prices? What events have influenced them in the past? This will help you plan ahead better. Developments in the electricity market are also important, as natural gas is central to electricity generation. Energy is a significant cost factor for many companies, and efficient energy management optimizes spending. Let's shape a low-carbon future together!
Our Expert